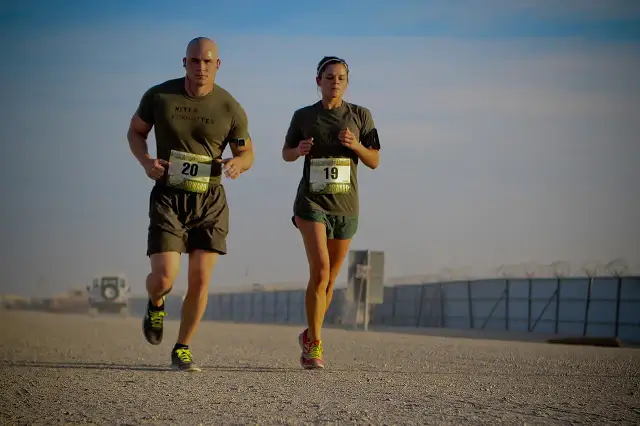
Do electrolytes help with cramps? Is drinking water enough to get rid of that sudden muscle spasm that you feel during sleep? Is dehydration really the cause of muscle cramps?
Yes, electrolytes can help with cramps. Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge and play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including muscle function. Therefore, if you are suddenly feeling cramps due to any reason (sports, exercise, other physical activities, or even during sleep), it is not because your body is dehydrated. In fact, drinking more water might actually worsen the cramp.
Let’s keep reading to know why we get cramps and how electrolytes can help you eliminate muscular cramps.
What Causes Muscle Cramps?
Muscle cramps often occur due to imbalances in electrolyte levels, especially when there is a deficiency of potassium, calcium, or magnesium. When you engage in intense physical activity, such as exercise or sports, your body may lose electrolytes through sweat. If these electrolytes are not adequately replenished, it can lead to muscle cramps.
Consuming foods or beverages that contain electrolytes can help maintain proper balance in your body, reducing the risk of cramps during physical activity. Sports drinks and electrolyte supplements are commonly used by athletes to help prevent muscle cramps and maintain hydration and electrolyte levels during prolonged exercise.
Athletes and Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps are a common and painful condition experienced by athletes across a wide range of sports, including around 39% of marathon runners, 52% of rugby players, and 60% of cyclists. It is a common misconception that dehydration causes muscle cramps. Contrary to popular belief, your body loses essential minerals through excessive sweating. If you drink water to take care of cramps, the water dilutes the remaining electrolytes making the muscles more prone to cramps. In most of the cases, muscle cramps can often result from a combination of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Addressing both these factors is crucial for effectively preventing and alleviating cramps.
Ensuring sufficient hydration and replenishing electrolytes through a balanced diet or electrolyte-enhanced beverages can help mitigate cramps during physical activity. By taking care of hydration and electrolyte levels simultaneously, you can better support your muscles and reduce the risk of experiencing painful cramps.
However, it’s also crucial to consider other potential causes of cramps, such as underlying medical conditions, nerve issues, medications, and nutrient deficiencies. If cramps are severe, recurrent, or interfering with daily life, seeking medical attention for a proper evaluation and personalized management is advisable.
Influence of Hydration and Electrolyte Supplementation on Muscle Cramps
Prevention of muscle cramps, especially if the cramps are exercise-induced, is of utmost importance. Research conducted by the University of Alabama has shown that the consumption of a carbohydrate-electrolyte beverage before and during exercise in a hot environment may delay the onset of exercise-induced muscle cramps (EAMCs), thereby allowing participants to exercise longer.
The influence of hydration and electrolyte supplementation on muscle cramps is significant, as both factors play crucial roles in muscle function and performance. Let’s examine their individual impacts and their combined effects:
Hydration:
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining the body’s fluid balance, supporting various physiological functions, including muscle function. Dehydration can lead to an imbalance of electrolytes in the body, making muscles more susceptible to cramps. When you are dehydrated, the concentration of electrolytes in your bloodstream can become more concentrated, increasing the likelihood of muscle cramps during physical activity.
Electrolytes:
Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, are essential for transmitting electrical signals that regulate muscle contractions. Imbalances in these electrolytes can disrupt nerve impulses and lead to muscle cramps. During intense exercise or prolonged physical activity, the body can lose significant amounts of electrolytes through sweat. If not adequately replenished, this can further increase the risk of muscle cramps.
Researchers from Edith Cowan University published a study in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition that explores how electrolyte-enhanced water helps prevent this condition. This can also reduce the risk of muscle cramps and also aid in muscle recovery after exercise.
The most popular sources of electrolytes include sports drinks, electrolyte-enhanced water, electrolyte tablets, and certain foods like bananas (potassium), dairy products (calcium), and nuts and seeds (magnesium).
Combined Effect:
Hydration and electrolyte balance are closely interconnected. Adequate hydration helps maintain proper electrolyte levels in the body, as fluids facilitate the transport of electrolytes to cells. On the other hand, proper electrolyte supplementation ensures that the body has enough of these minerals to support muscle function. By addressing both hydration and electrolyte levels simultaneously, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of muscle cramps during exercise.
Tips to Prevent Muscle Cramps:
If you experience persistent or severe cramps, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. However, it’s essential to note that not all cramps are caused by electrolyte imbalances. Dehydration, muscle fatigue, and other factors can also contribute to cramping. Meanwhile, let’s have a look at some common tips that will help you prevent muscle cramps.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink sufficient water before, during, and after physical activity to maintain optimal hydration levels. While dehydration is not the primary cause of cramps, it surely contributes to the healthy and efficient working of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles.
Consume Electrolytes:
Include foods rich in potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium in your diet. Alternatively, consider using electrolyte-enhanced sports drinks or supplements during intense exercise to replenish lost electrolytes. You can find some great electrolytes and hydration drops here.
Warm-Up and Stretch:
Failing to do a proper warm-up session can induce muscle cramps. Properly warm up before exercising and stretch afterward to help prevent muscle fatigue and cramps. This also includes taking your pre-workout electrolytes and making sure that your muscles are ready for the exertion.
Monitor Your Activity:
Avoid overexertion and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Especially if you experience recurring cramps you should allow your muscles to rest and recover before moving on to the next exercise.
Rest and Recovery:
Allow your muscles adequate time to rest and recover between intense exercise sessions. If you experience severe or frequent cramps during exercise, it’s essential to pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust your workout routine as needed.
Seek Medical Advice:
If you experience frequent or severe muscle cramps despite proper hydration and electrolyte balance, consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Electrolytes play a significant role in helping with cramps, especially muscle cramps that often occur during physical activity. They help ensure smooth muscle contractions and nerve signaling, preventing spasms and involuntary muscle contractions that lead to cramps. By replenishing electrolytes through proper nutrition or electrolyte-enhanced beverages, you can maintain a balanced electrolyte profile, thereby reducing the risk of muscle cramps.
However, it’s essential to remember that not all cramps are solely caused by electrolyte imbalances. Other factors such as muscle fatigue, overexertion, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute to cramping. Therefore, maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte levels, along with overall muscle health, is essential for effectively preventing and managing cramps during physical activity. If cramps persist or are severe, seeking medical advice is advisable to identify any underlying issues and receive appropriate treatment.