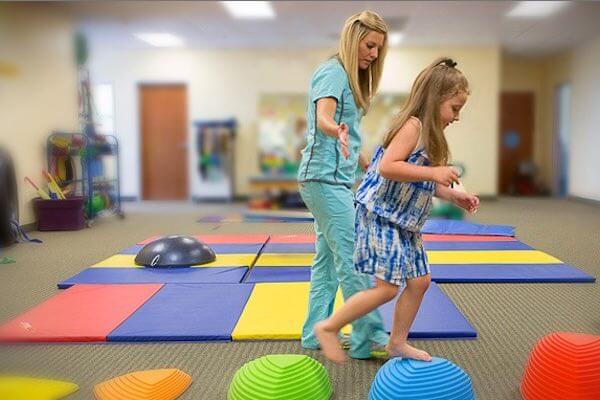
Physical therapists are trained in advance and movement dysfunction to support strengthen a patient’s physical abilities especially joint specialist. They help reduce Traumatic Brain Injuries through the use of therapeutic exercise, heat, cold and electrical stimulation.
PTs also present expertise in human mobility, analyzing gait patterns, prescribing treatment and suggesting devices (such as braces or crutches) to allow independent movement. By increasing coordination, strength and endurance, a PT can treat a patient to recover from physical injuries and impairments.
PTs are specialists in assessing and treating disorders of the human body by utilising physical means rather than drugs. They are professionally and ethically responsible for planning, implementing and evaluating a physical therapy program.
This responsibility often involves instructing patients and their families and managing physical therapist assistants, physical therapy aides, students and other health care workers in taking out the program or selected parts of it.
The PT consults and works similarly with the patient’s physician and other health care practitioners in discovering treatment objectives, which are practical and consistent with the patient’s needs. They also present services aimed at preventing the onset and slowing the progress of conditions resulting from injury, disease and other problems.
The traumatic brain injury (TBI) people are one of the most challenging that a physical therapist may meet. Because of the multiple body systems influenced by a brain injury and the strong likelihood of secondary impairments, a physical therapist must be expert in a wide variety of examination procedures and intervention techniques.
Owing to behavioural problems encountered during recovery, a PT working with the TBI people must also possess strong interpersonal skills, be able to react immediately and adequately to suddenly changing situations, and have keen observation abilities.
People with brain injuries are treated across a wide continuum of care, which involves acute hospitalization, rehabilitation centres, community reentry programs, schools, outpatient therapy, vocational rehabilitation, and assisted living centres.
At Rainbow, the patient with brain injury helps from having most of these settings at the same place. Because a number of impairments and difficulties arising from a brain injury, it is vital that a strong team idea is employed when treating this population. APT is an essential member of this team and works with a wide variety of neuromuscular, visual, cognitive, perceptual and behavioural impairments that lead to practical limitation and disability.
How Does Physical Therapist Works?
PTs work on soft tissue mobilization as well as a range of motion exercises beginning on after the injury to support joint integrity and mobility and limit contractures. Positioning strategies are also essential for more dependent patients who require assistance to maintain soft tissue length. They also correlate with family and caregivers for long-term management.
Pediatric physical therapy also utilises neurodevelopmental treatment (NDT) with the TBI population. NDT maintains postural control for all skill learning. Normal movement models are encouraged, excessive tone and abnormal movements are inhibited, and activities that are functionally related and varied in terms of difficulty and environmental context are preferred.
Compensatory instruction, which allows the use of the less involved segments (lower and upper extremities) more than affected parts is discouraged, and carryover is promoted through strong stress on patient, family and caregiver education.
Inhibition of falls for this population, which has a huge incidence of balance deficiency, is an essential goal of therapy. Lifestyle counselling is necessary to help recognize potentially dangerous situations and reduce the likelihood of falls. Substantial recovery efforts are directed toward enhancing gait to restore or improve a patient’s functional mobility and independence. Walking is usually the number one goal of patients above all other considerations.