What is monkeypox? What are its symptoms and causes? In this article, you will learn about the symptoms and causes of this disease. Then, read on to learn about the signs and wounds caused by monkeypox. You’ll also discover what to do if you or someone you love gets the illness. It is a viral infection that causes skin lesions. A person who gets monkeypox usually has no signs of the disease, but it can be quite severe for those with a weakened immune system.
What Is Monkeypox?
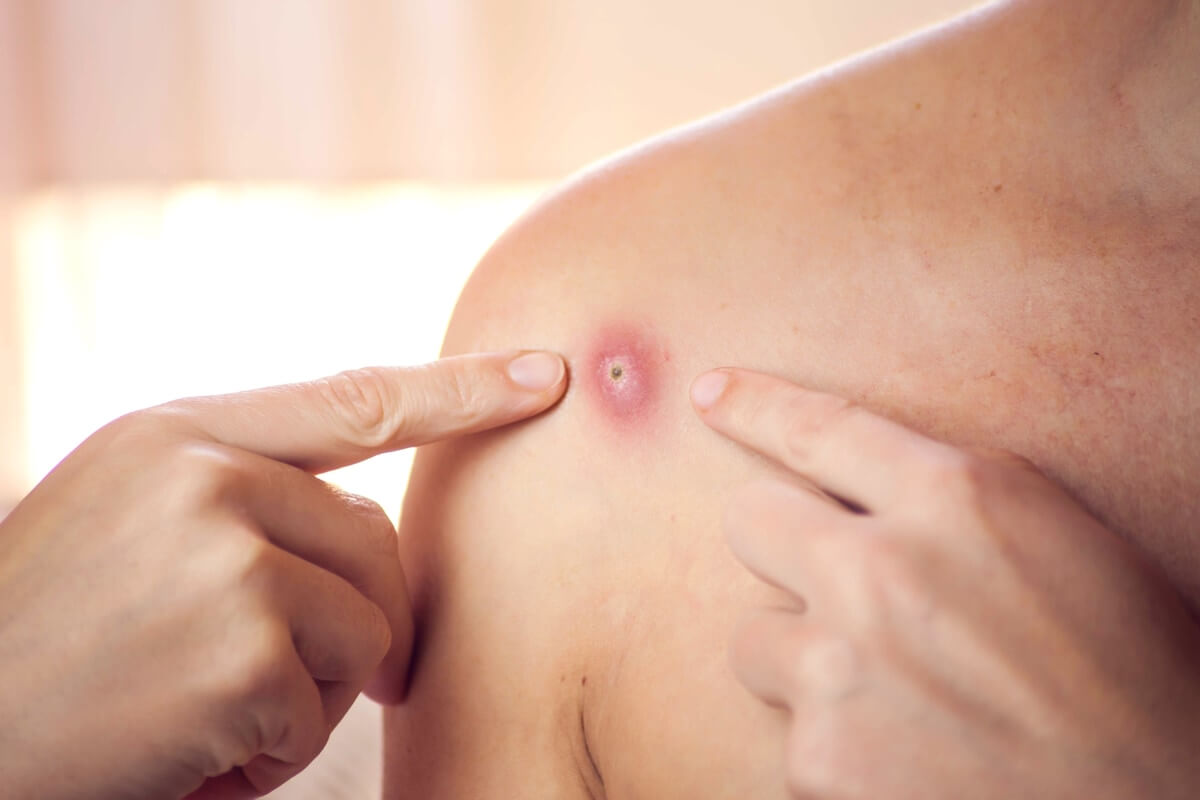
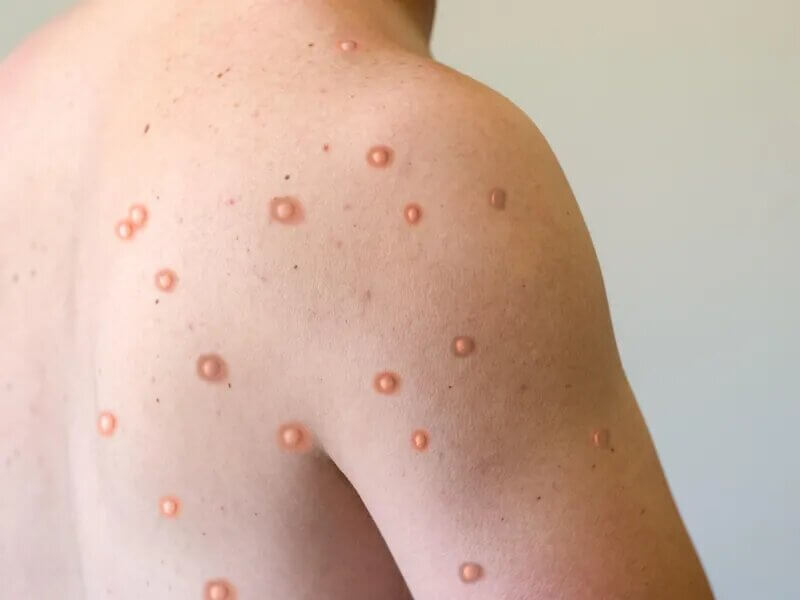
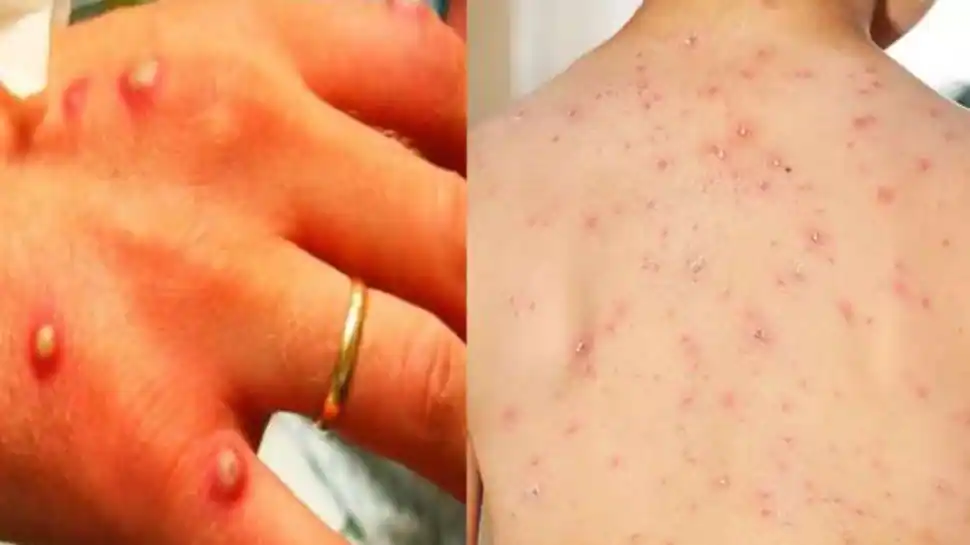
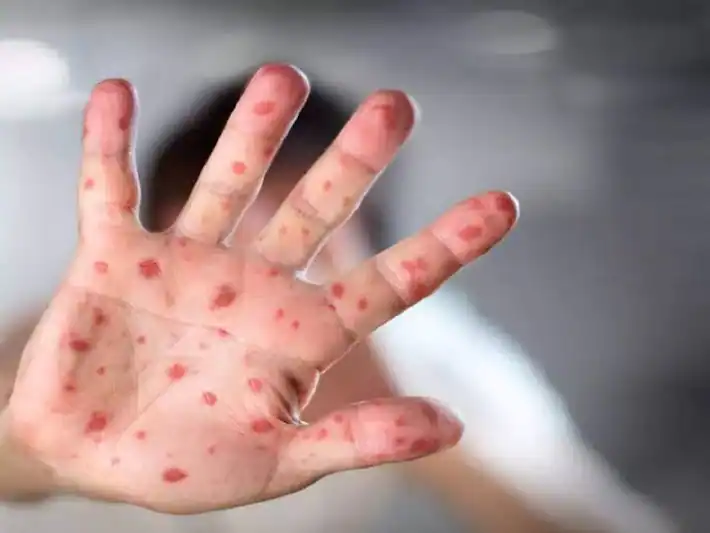
What is monkeypox? Monkeypox is a common skin infection. Symptoms typically start with flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, and general body aches. The rash will then develop. Finally, the sores will resemble pimples and go through different stages before they heal. It can appear anywhere on the body, including the genitals, chest, and hands. While symptoms of monkeypox are often challenging to detect, a health care provider can help.
If you suspect you have monkeypox, you should contact your health care provider for an examination. Your health care provider may want to obtain a blood sample or a lesion for further testing. If you have the symptoms of monkeypox, your doctor will most likely recommend sending a sample for a PCR test. However, we can only do this test in specialized labs.
The disease is generally mild and runs for two to four weeks. However, it can be dangerous for children or people with weakened immune systems. It can also be fatal, affecting as many as 1/10 people, especially in Africa. The only way to prevent monkeypox is to get vaccinated before traveling to areas with a high risk of it. However, if you travel to Africa, it is crucial to seek proper treatment.
What Is the Cause of Monkeypox?
Like smallpox, monkeypox can be fatal for some people. While the disease can run its course in 2 to 4 weeks, it is hazardous for people with weak immune systems and young children. The symptoms of monkeypox include fever, swollen lymph nodes, and a general feeling of discomfort and exhaustion. A widespread rash develops about one to three days after the initial fever. The rash typically appears on the face.
Because monkeypox causes a rash, a health care provider may suspect another illness as the cause of the rash. However, monkeypox is distinguished from other poxes by swollen lymph nodes and rash. Your healthcare provider may also order a blood sample to test for antibodies to the monkeypox virus. It is important to note that you may experience several symptoms of monkeypox, so it is best to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
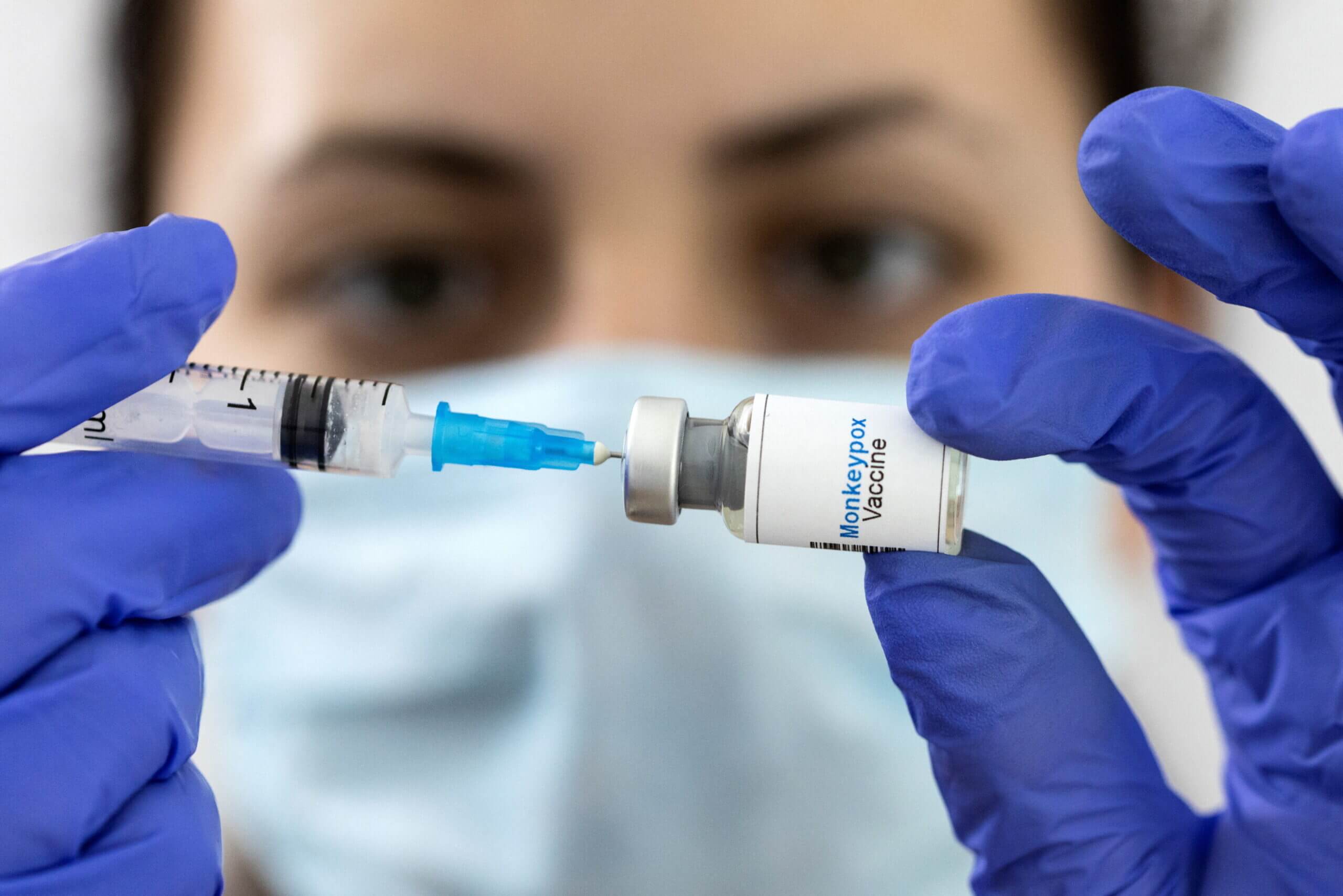
The CDC recommends that people who have had contact with monkeypox receive the vaccine within four days of exposure. However, this vaccine may be administered as late as 14 days after exposure. A vaccination against monkeypox will significantly reduce symptoms and can prevent you from contracting the disease in the future. When is monkeypox contagious? Can spread infections of the skin, mucous membranes, and respiratory secretions.
What Are the Symptoms of Monkeypox?
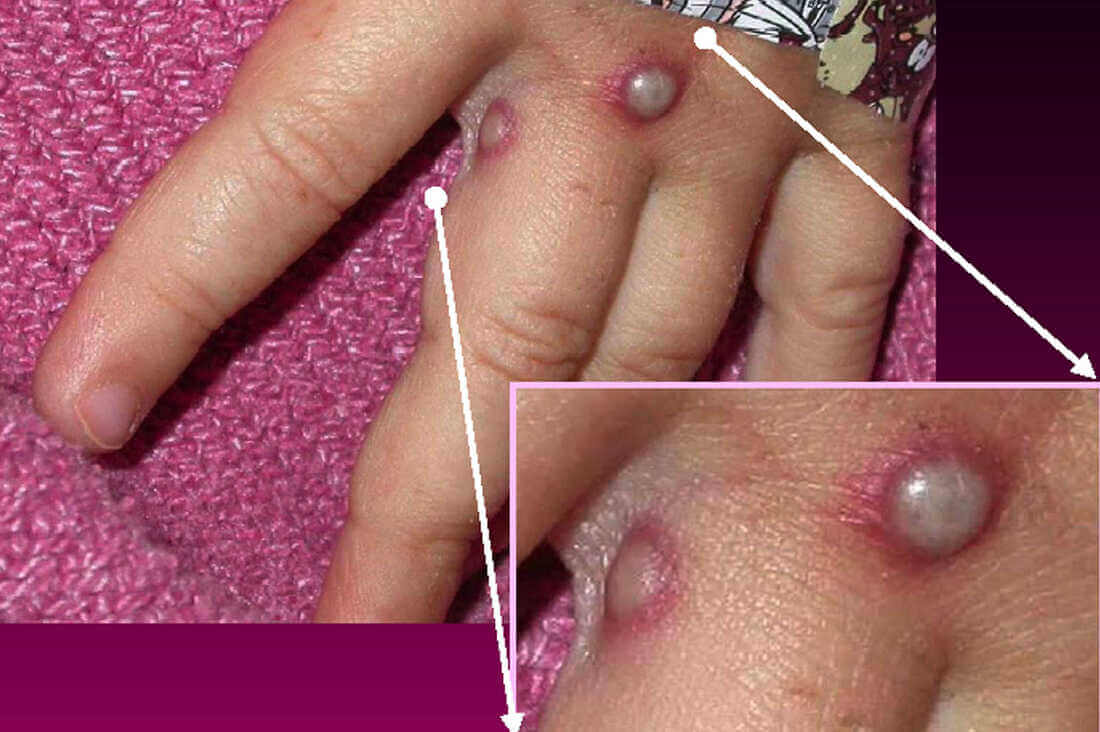
Symptoms of monkeypox are similar to those of smallpox but are milder and usually not fatal. The first cases were confirmed in only one person, and there have been no reports of death due to it. The rash starts as flat lesions called macules. These lesions eventually turn into pustules and blisters. However, they are not immediately apparent. If you suspect you have monkeypox, contact your local health department to get the proper treatment.
Initial symptoms of monkeypox include fever, muscle aches, and flu-like symptoms. It is typically accompanied by a blister-like rash that begins on the face, then spreads to the rest of the body. The lesion is usually red and fluid-filled and may start on the face but may also affect the genital area. It can be fatal in up to 6% of cases.
Wounds Caused by Monkeypox Go Through the Following Stages Before They Heal
The most crucial part of treating wounds caused by monkeypox is early diagnosis. Unlike some other infectious diseases, the illness usually resolves on its own. Symptomatic treatment focuses on maintaining the patient’s health and preventing the blisters from breaking. Symptoms of monkeypox infection are typically not itchy, but they may become irritated or even painful when healing.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that all individuals experiencing symptoms of monkeypox seek medical attention. If you have visited monkeypox-endemic countries, come into contact with an infected monkey, or live in close contact with an infected man, see your doctor immediately. Treatment for monkeypox varies depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s condition.
Symptoms of monkeypox include fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes. It takes five to 21 days to develop the illness. Symptoms can occur anywhere on the body, including the face. Patients may be infected with monkeypox by prolonged face-to-face contact with an infected person. It can also be contracted indirectly through contaminated items, such as bedding, towels, or clothing.
Can Having Sex Cause Monkeypox?
Can having sex cause a moneybox? Yes, it can. This infectious disease is spread through close contact with a person with the virus. It is also transmitted through the respiratory tract and body fluids. However, it is more common in men than in women. So, the question remains: Is it safe to have sex during an outbreak? Let’s find out. The most common source of this virus is skin-to-skin contact, which is highly spread through sexual intercourse.
Generally, men with a recent outbreak of monkeypox are at a lower risk of developing the illness than women who have had multiple partners within the last two weeks. Symptoms of monkeypox usually begin within three weeks of exposure and last for two to four weeks. Most people experience a rash and painful lesion that typically require hospitalization. The symptoms may be mild or severe enough to be life-threatening.
How Is Monkeypox Spread?
It is a relatively rare disease primarily found in central and western Africa. Scientists first discovered monkeypox in 1958, but it was not known to affect humans. Until the spring of 2022, it had only been found in monkeys in the wild and had only been reported in humans from other parts of Africa. But since then, the disease has been identified in humans, resulting in an outbreak that has led to at least 70 cases in the U.S.
Monkeypox has a low incidence in humans but is still highly contagious. To contract monkeypox, a person must be exposed to the disease for at least three hours within six feet. The condition is also spread through contact with contaminated clothing and linen. The World Health Organization says that monkeypox is not endemic in the U.S. but would consider a change in their position if they found that more cases spread from person to person via droplet transmission.
What Are the Clinical Features of Monkeypox?
It is a smallpox-like illness caused by a zoonotic orthopoxviral infection. Its first documented human cases occurred in 1970 in central Africa. It is endemic in the Congo basin and West Africa, with most human cases occurring in the Congo. The disease is rarely reported in developed countries, but outbreaks can challenge epidemiologic investigations.
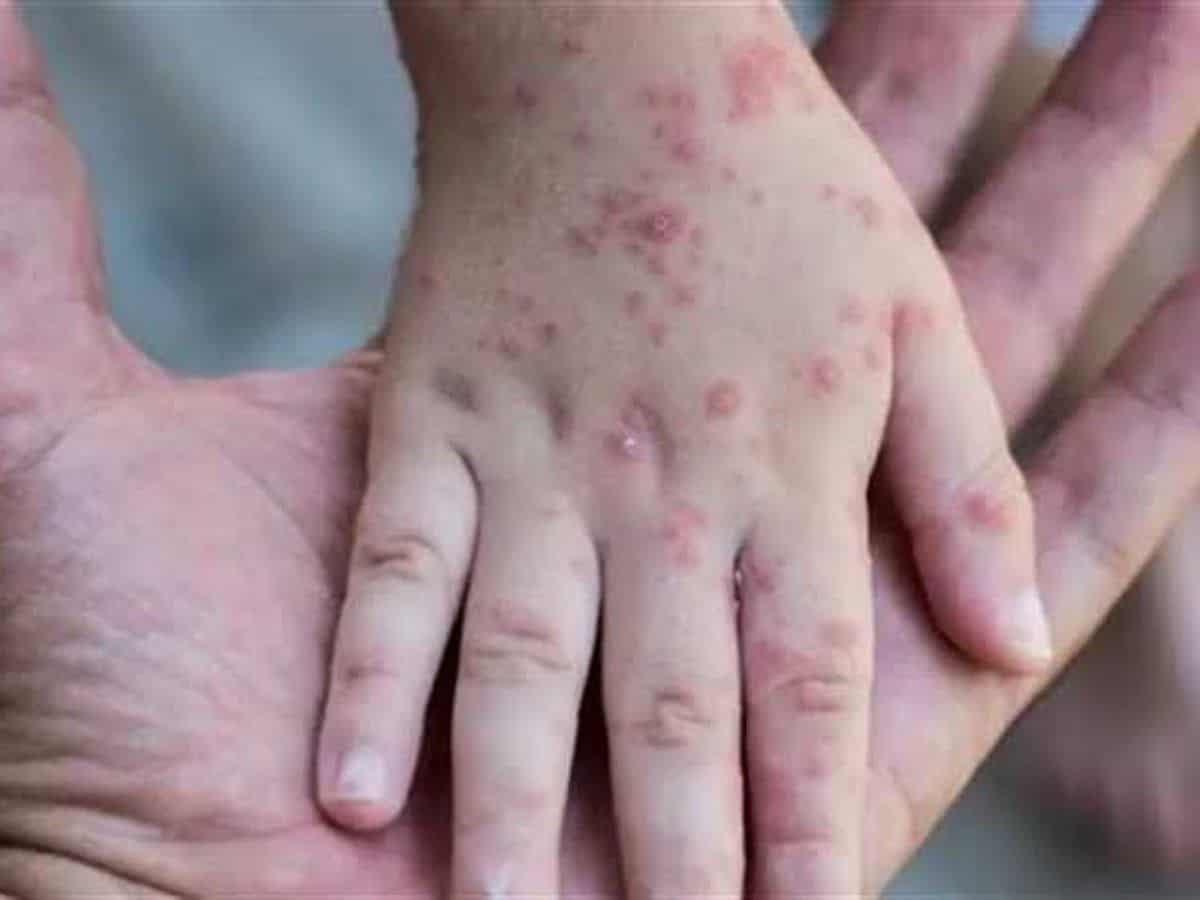
The typical clinical symptoms of monkeypox are fever, general body aches, and muscle aches. The sores form on the affected part of the body and progress to several stages before they heal. The rash may appear in the genitals, hands, or chest, but it may be located on other parts of the body, such as the groin. While there is no cure for monkeypox, it is an uncomfortable and painful illness that may require medical attention.
While the disease is rare in the U.K., it poses unique challenges for health care systems. The prolonged shedding of viral DNA during the upper respiratory tract has challenged current guidelines for infection control. In addition to clinical symptoms, It may lead to secondary bacterial infections or pneumonitis. Therefore, it is a high-consequence infectious disease (HCID). It cases are typically managed in a hospital or clinic treating patients with monkeypox.
Is Monkeypox Fatal?
Most patients develop the disease after contacting an infected animal, such as a prairie dog. But some cases may have been infected by other animals such as rabbits or Gambian giant rats, which were bought as pets. It can also be contracted by touching an animal’s bodily fluids or contaminated bedding. In addition, although the disease is not fatal, it can spread through close contact with active rashes.
A virus caused by monkeypox is called orthopoxviral. It is similar to smallpox but different from the COVID-19 virus. It is endemic in certain parts of Africa and has only recently been found in human cases. However, the virus is also present in sporadic clusters throughout the world. Transmission is sometimes associated with international travel or contact with infected animals.
The West African strain of the monkeypox virus is not fatal for most people, with 99% of cases resulting in a full recovery. However, people with weakened immune systems or other conditions, such as eczema, pregnancy, and breastfeeding, are at higher risk for serious illness. In addition, the disease can cause painful and permanent scarring, so it is vital to seek medical care as soon as possible. Unfortunately, there is no cure for monkeypox, but the West African strain is known to be very contagious.
Why Is the Monkeypox Virus Spreading So Fast?
While the disease is endemic to several parts of the world, it has become an increasingly dangerous threat as cases have appeared outside the usual locations. Among other things, people who were not traveling to endemic areas suddenly became infected. Scientists are trying to discover why the virus is spreading so fast, and one expert explains how countries should be prepared. “As a medical professional, I have a unique perspective and see this as an opportunity to learn more about the disease. So I’m glad to be doing this,” says Dr. Toner.
Researchers are studying how the virus acquired its ability to jump between different animals, which may explain the current outbreak. The current strain is genetically similar to the strain that caused the 2017 outbreak in Nigeria. Further sequencing of the virus will help answer this question and determine the adaptation of the virus’s genome for human infection. But for now, the question remains, “Why is the monkeypox virus spreading so fast?”
How Is Monkeypox Different from Smallpox or Chickenpox?
A common question is: “How is monkeypox different from chickenpox or smallpox?” Both forms have similar symptoms and are spread through skin-to-skin contact. The primary difference between the two types of infections is the incubation period. Monkeypox usually lasts seven to 14 days. The rash typically begins one to three days before the other symptoms are visible. Both lesions progress through several stages before forming a scab. Monkeypox usually starts on the face, but it can spread to other body parts, including the arms, legs, palms, and soles. Both lesions can affect the face and tongue, but monkeypox usually produces a mild illness.
The primary method of transmission is through unprotected contact with the infectious agent. This means avoiding unprotected contact with wild animals. Must cook foods containing animal parts before consumption. In addition, certain countries restrict the import of non-human primates and rodents, which may cause the spread of monkeypox. When you encounter a monkeypox-infected animal, you should immediately quarantine the animal. Use standard precautions when handling the animal, and monitor it for at least 30 days after the initial infection.
Will Monkeypox Be the Next Pandemic?
There’s a chance that monkeypox could become the next pandemic. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared a pandemic in January 2020. Two months later, the organization declared the Covid-19 epidemic a pandemic. The WHO has no formal process for declaring a pandemic, but it has a very loose definition of the disease.
It has been detected in countries where the disease has been eradicated. Many possible reasons include climate change and increased human-wild animal contact. In addition, growing populations and habitats of certain animals that carry zoonotic viruses have contributed to the spread of monkeypox. Climate change has also played a role in the increasing prevalence of monkeypox.
While the virus is not very contagious, it is close to the one that caused recent outbreaks in 2018 and 2019. The virus was exported from Nigeria to several other countries, and it appears to be less contagious. Previously, believed that the disease was primarily transmitted from human to animal, with only a few human cases. However, there have been outbreaks recently where humans are infected with the virus.
Who Is at Risk of Getting Monkeypox?
People can be exposed to monkeypox by close contacts, such as by sharing towels, clothing, and toilet paper. Although this disease is rare, some countries, including thU.S.US, have increased rates of monkeypox cases. In addition, men who are gay, bisexual, or have sex with men are at risk. Therefore, men who have come in contact with an infected person should tell their healthcare provider about their exposure and avoid close physical contact with those with the disease.
Although there are no known cures for monkeypox, most people recover without treatment. You should visit a health care provider immediately if you notice any of these symptoms. They can examine your symptoms and order tests if necessary. People with the disease are contagious until all the sores heal and a new layer of skin forms. They should avoid sexual intercourse with infected individuals until they are fully recovered.
Is Monkey Pox Airborne?
Monkeypox is not considered airborne, although it is a risk to humans. The CDC reported 45 cases in 15 states, plus WashingtonD.C.C. The current outbreak is not associated with international travel, and no deaths have been reported. It is transmitted through physical contact with infected individuals and their respiratory secretions, semen, and vaginal fluids.
The virus can also be airborne if present in infected individuals’ saliva and respiratory secretions. In addition, the virus can float on the air currents and infect people who enter a room after the infected person leaves. Aerosols may carry monkeypox in the respiratory system or saliva or respiratory secretions. Neither method has been proven, but the CDC will continue to monitor the situation and make recommendations as more research is done.
Monkeypox can also be spread by respiratory secretions and sustained face-to-face contact. Because of the high risk of spreading the disease to others, the CDC has urged healthcare providers to use surgical masks to protect their patients from the disease. However, doctors can’t be sure that monkeypox will spread through the air. Therefore, in cases where there are multiple cases, medical professionals recommend wearing surgical masks.
Is There Any Reason to Think Monkeypox Is Seasonal?
The virus that causes monkeypox is in the same genus as smallpox, and both viruses are large DNA viruses with a specific appetite for skin tissue. While smallpox primarily affected humans, virtually eradicated through mass vaccination. Monkeypox is also carried by an animal viral reservoir but not by monkeys themselves. As a result, it’s not considered seasonal.
In 1980, the Global Commission for Certification of Smallpox Eradication (GCCES) listed MPX as the most crucial orthopoxvirus infection in men and recommended a surveillance program. Several studies have reported varying cases, with Jezek et al. reporting 132 cases from 1981-1983. However, the numbers may not be accurate.
In recent years, the number of cases of monkeypox in thU.S.S. has risen. In 2021, two cases were linked to Nigeria, and 47 were linked to Ghana 2003. The recent global outbreaks have been linked to animals imported from Ghana and other European countries. However, the Institut Pasteur Paris studies monkeypox’s anthropological and zoological factors.
Should India Worry About Monkeypox?
Should India worry about monkeypox symptoms? Health experts stressed a recent spike in monkeypox cases in other countries. However, despite the risk of the disease spreading, there are definite guidelines for treatment and prevention. Infected people are contagious only during incubation, and the disease can spread through close contact with respiratory droplets, skin lesions, or recently contaminated objects.
There have been no reported fatalities from monkeypox in the general population in India. While it is still highly contagious, its occurrence in the country is unlikely to alarm Indian health officials. Although the infection may be transmitted to humans, the risk of complications is small and can be easily avoided with vaccination. In addition, symptomatic treatment of monkeypox can help the patient recover faster. Although there is no specific treatment for monkeypox, doctors recommend that people with the disease seek medical attention for any possible complications.
Symptoms of monkeypox include pimple-like lesions and flu-like symptoms. It is transmitted through close contact and respiratory droplets. It can even pass through the placenta. Therefore, travelers should be cautious before visiting India. But what should they know about the symptoms and treatment? In the meantime, stay away from monkeypox-infected countries. If you have never had the disease, it may be worth taking the abovementioned precautions.
How Is Monkeypox Diagnosed?
When is monkeypox diagnosed? In general, monkeypox symptoms start two to three days after exposure to the virus. Symptoms of monkeypox include fever and flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, and fever. In addition, sores and rash may appear in severe cases on the chest and hands. It symptoms can also affect the genital area.
Treatments for monkeypox depend on the severity of the symptoms. Generally, it requires rest and should not be spread to others. Patients should isolate themselves and avoid crowds until they are fully recovered. Treatment may include over-the-counter meds for pain, rest, and swollen lymph nodes. You should call your healthcare provider if you develop any of these symptoms. If you think you have monkeypox, contact your health care provider right away.
A physician will confirm monkeypox infection by examining a sample of the skin and DNA from the patient. If the skin sample reveals signs of it, your doctor may order a PCR test to determine the presence of the virus. PCR tests are only available at highly specialized laboratories, so if you are unsure, isolate yourself at home. Do not share your needles with others until you are sure you have the virus.
How Is Monkeypox Treated?
How is it treated? It is a common question in the minds of travelers. While monkeypox is generally mild, its symptoms are infectious and can spread quickly. Therefore, people with the disease should seek treatment as soon as possible and report their symptoms to medical staff to follow proper quarantining procedures. The rash may be irritated and sore, and you may experience pain while defecating or urinating.
The infection is spread by direct contact with the lesions of an infected person with the virus. For example, you can get monkeypox by scratching or interacting with contaminated materials. You can also get monkeypox through animal-to-human transmissions, such as from a bite or scratch. A person can also contract monkeypox from eating bush meat. You can also get monkeypox through respiratory droplets from someone with the virus. This form of transmission requires prolonged face-to-face contact. Symptoms of monkeypox include rash, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
The most common symptoms of monkeypox are rash and fever, but you should not be alarmed if you do not have any of these symptoms. It is difficult to tell the difference between monkeypox and other poxes, so your healthcare provider may suspect something else. If the rash is associated with lymph nodes, your healthcare provider will examine it under the microscope and determine whether it is monkeypox. They may also ask for a blood sample to check if you have antibodies to the virus.
Is It Possible to Prevent Monkeypox Virus?
The virus that causes monkeypox is easily spread among humans, especially during close contact. The disease is most likely to spread through close contact with infected bodies, such as the nose, mouth, and eyes. It can also be passed from person to person through respiratory secretions during prolonged face-to-face contact. While the disease is not sexually transmitted, it can still spread through close contact, so it is imperative to seek medical attention and wear protective masks.
If you don’t have access to healthcare, visit a public health clinic or your county’s health department to get an immunization. Then, avoid crowds and close contact with infected people, especially if you’re sexually active. If you’re unprotected, consider getting a monkeypox vaccine. These vaccines can protect you against the disease if given before or within a few hours after exposure to the virus. You can choose between the JYNNEOS vaccine or ACAM2000.
It’s important to check for lesions of monkeypox if you’re infected. These lesions look similar to chickenpox and can be challenging to diagnose. They can also be a divot in the center. If you notice a divot in a skin lesion, you should have it checked out immediately. In the meantime, you can rest easy knowing that this disease is not widespread and the risk is minimal.
You can also consult a doctor for more information in this regard.